Docker-compose for microservices development
A microservice is a small, loosely coupled distributed service. Microservice Architectures evolved as a solution to the scalability and innovation challenges with Monolith architectures (Monolith applications are typically huge – more 100, 000 line of code). It allows you to take a large application and decompose or break into easily manageable small components with narrowly defined responsibilities.
Reasons for using Microservice:
In monolith application, there are few challenges:
- For a large application, it is difficult to understand the complexity and make code changes fast and correctly, sometimes it becomes hard to manage the code.
- Applications need extensive manual testing to ensure the impact of changes.
- For small change, the whole application needs to be built and deployed.
- The heavy application slows down start-up time.
Benefits of Microservices:
- Small Modules – Application is broken into smaller modules which are easy for developers to code and maintain.
- Easier Process Adaption – By using microservices, new Technology & Process Adaption becomes easier. You can try new technologies with the newer microservices that we use.
- Independent scaling – Each microservice can scale independently via X-axis scaling (cloning with more CPU or memory) and Z-axis scaling (sharding), based upon their needs.
- Unaffected – Large applications remain largely unaffected by the failure of a single module.
- DURS – Each service can be independently DURS (deployed, updated, replaced, and scaled).
Based on same Principle i am building Shopping Cart Application
- Node js
- Redis
- Mysql
- Cart APIs
- Checkout APIs
- Order APIs
We will need all these application to run and docker-compose can help us in building all these containers in one common network
Docker Compose
It’s a command-line tool that allows you to automate configuration and management of containers for complex applications running with Docker. It works by processing configuration file that you define (i.e. docker-compose.yml), and makes it possible to bootsrap full suite of your services in one command: docker-compose up
Cart Application
"It's just simple application to provide REST APIs for mini e-commerce platform where individual can buy products and can pay the bills
- microservices architecture
- Client application in React
- User Auth microservices
- Cart services
- Admin Microservices
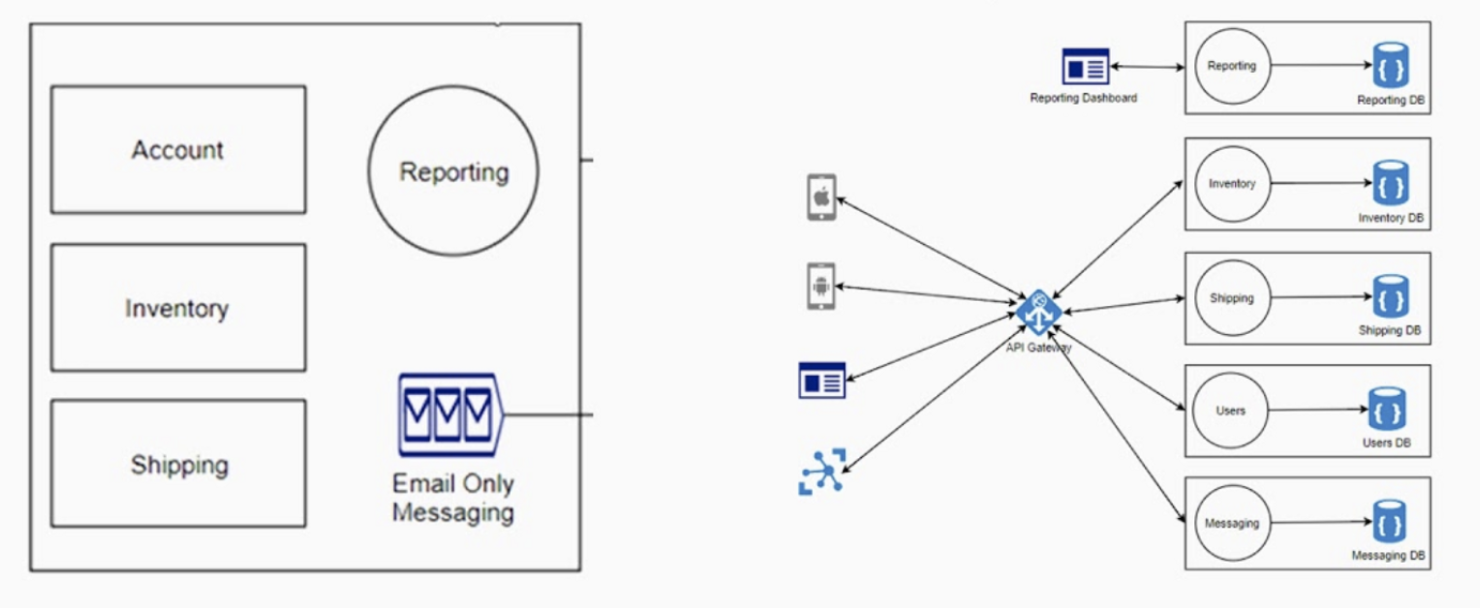
We can write one common docker-compose file and spin all services which are already built and ready to be deployed or tested
version: '3.5'
services:
gateway:
image: nginx:1.11
ports:
- 80:80
- 443:443
volumes:
- ./proxy/default.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf:ro
- ./proxy/ssl:/etc/nginx/ssl:ro
depends_on:
- ms_commerce_auth
- ms_commerce_admin
- ms_commerce_client
networks:
- ms_network
ms_mysql:
container_name: ms_mysql
image: mysql:5.7
volumes:
- ~/datadir/mysql:/var/lib/mysql
ports:
- 3306:3306
- 33060:33060
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
networks:
- ms_network
ms_commerce_mongo:
image: mongo
container_name: ms_commerce_mongo
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- ~/datadir/mongo:/data/db
ports:
- 27017:27017
networks:
- ms_network
ms_commerce_auth:
container_name: ms_commerce_auth
build: ./e-Commerce-Auth/
image: e-commerce-auth
volumes:
- ./e-Commerce-Auth/:/usr/src/app
- /usr/src/app/node_modules
ports:
- 3001:3001
- 9201:9201
depends_on:
- ms_mysql
networks:
- ms_network
ms_commerce_cart:
container_name: ms_commerce_cart
build: ./e-Commerce-Cart/
image: e-commerce-cart
volumes:
- ./e-Commerce-Cart/:/usr/src/app
- /usr/src/app/node_modules
ports:
- 3004:3004
- 9204:9204
depends_on:
- ms_mysql
networks:
- ms_network
ms_commerce_admin:
build: ./e-Commerce-Admin/
image: e-commerce-admin
container_name: ms_commerce_admin
environment:
- NODE_ENV=local
volumes:
- ./e-Commerce-Admin/:/usr/src/app
- /usr/src/app/node_modules
ports:
- 3002:3002
- 9202:9202
depends_on:
- ms_commerce_mongo
networks:
- ms_network
ms_commerce_client:
build: ./e-Commerce-Client/
image: e-commerce-client
container_name: ms_commerce_client
environment:
- NODE_ENV=local
volumes:
- ./e-Commerce-Client/:/usr/src/app
- /usr/src/app/node_modules
ports:
- 3003:3003
depends_on:
- ms_commerce_admin
- ms_commerce_auth
networks:
- ms_network
networks:
ms_network:
driver: bridge
name: ms_networkWe are using all these different containers and docker-compose is running them in one netrwork so they can talk to each other
- like node js service talking to mysql
- like node js service talking to redis
- front end application talking to node JS
Routing of request from UI
We have nginx container running and we can do reverse proxy with it to talk to different services
A Nginx HTTPS reverse proxy is an intermediary proxy service which takes a client request, passes it on to one or more servers, and subsequently delivers the server’s response back to the client. While most common applications are able to run as web server on their own, the Nginx web server is able to provide a number of advanced features such as load balancing, TLS/SSL capabilities and acceleration that most specialized applications lack. By using a Nginx reverse proxy all applications can benefit from these features.
Benefits of Using a Nginx Reverse Proxy on an Instance There are a important benefits of setting up a Nginx HTTPS reverse proxy:
- Load Balancing: A Nginx reverse proxy can perform load balancing which helps distribute client requests evenly across backend servers. It also improves redundancy as if one server goes down, the reverse proxy will simply reroute requests to a different server according to the routing policy.
- Increased Security: A Nginx reverse proxy also acts as a line of defense for your backend servers. - Configuring a reverse proxy ensures that the identity of your backend servers remains unknown.
- Better Performance: Nginx has been known to perform better in delivering static content file and analyse URLs
- Easy Logging and Auditing: Since there is only one single point of access when a Nginx reverse proxy is implemented, this makes logging and auditing much simpler.
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/pac.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/pac.key;
server {
server_name ms-commerce.com;
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
location / {
proxy_pass http://ms_commerce_client:3003;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://ms_commerce_auth:3001/api/;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $server_name;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
location /admin/ {
proxy_pass http://ms_commerce_admin:3002/api/;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $server_name;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
location /cart/ {
proxy_pass http://ms_commerce_cart:3004/api/;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $server_name;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
}you can update /etc/host file to ping ms-commerce.com as local application
update etc/hosts file
##
# Host Database
#
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
# when the system is booting. Do not change this entry.
##
127.0.0.1 localhost
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhost
127.0.0.1 mysql redis mongo
127.0.0.1 ms-commerce.comSevices end-point (nginx routing)
- http://ms-commerce.com/api/v1 Auth services
- http://ms-commerce.com/admin/v1 Admin APIs
- http://ms-commerce.com/admin/v1 Cart APIs

Comments